S7 200 Modbus Slave Library Download
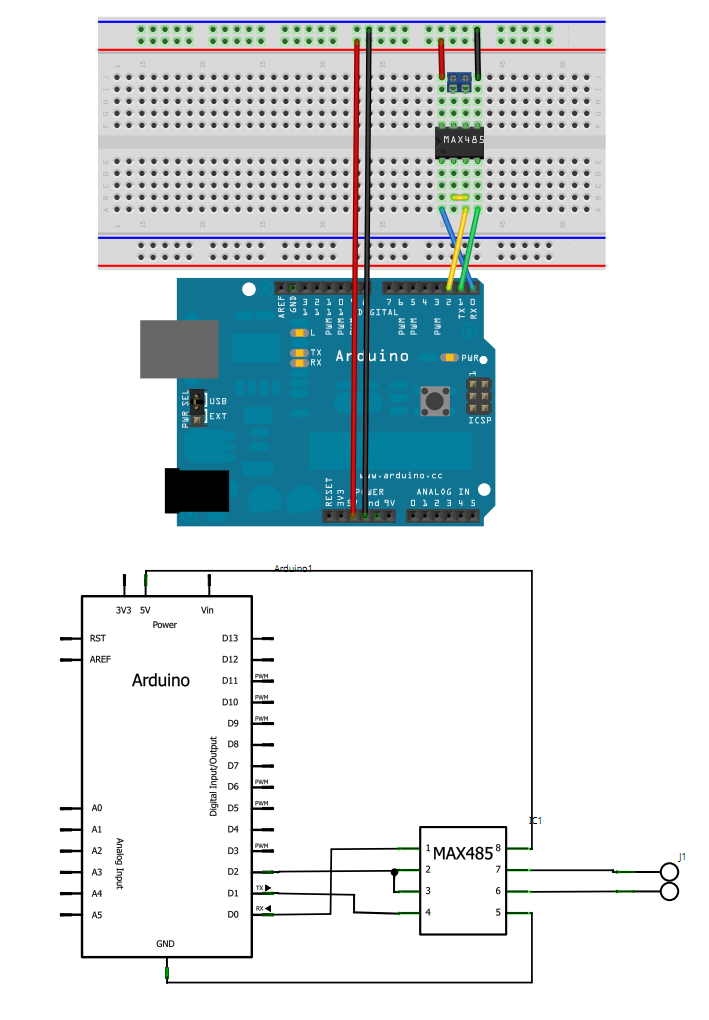
Modbus Slave & Modbus Master in S7 Refer to the Modbus Serial Pack v2 zip. Project Modbus v2 Manuals for drivers and hardware Preperation Preparation. To enable the Modbus functionality of the CP cards, you must do three things: Install Point to Point software from Install Modbus Master and Slave drivers from Fit the Modbus dongle to the rear of the CP Install the driver to the CP Preperation Summary of the GOULD-MODBUS Protocol The type of data exchange between MODBUS systems is controlled by Function Codes (FCs).
• The S7-200 CPU must be firmware revision 2.00 or greater to support the Modbus Master Protocol Library (CPU MLFB 21x-2xx23-0XB0). • The Modbus master library utilizes the user interrupts for some functions. Modbus plc simulator free download. PLC S7-200 Simulator WinCC6 Free version with data type: bit, byte, counter, timer. Download example here.
The following FCs can be used to carry out data exchange bit-by-bit: FC 01 Read coil (output) status, FC 02 Read input status, FC 05 Force single coil, FC 15 Force multiple coils. Shutochnaya prisyaga na vernostj kompanii. The following FCs can be used to carry out data exchange register-by-register: FC 03 Read holding registers, FC 04 Read input registers, FC 06 Preset single register, FC 16 Preset multiple registers.
Gould-Modbus Summary of the GOULD-MODBUS Protocol It will save considerable time and frustration to have a good idea upfront of the mapping of Modbus data to S7 data. The Modbus slave will define the function codes to be used by virtue of the fact that specific data is held in specific Modbus registers. Function Code Modbus Address Range Access Output Coils Function Codes 01, 05, 15 Read/Write Input Coils Function Code 02 Read Only Internal Registers Function Code 04 Holding Registers Function Codes 03, 06, 16 Gould-Modbus Configure the Hardware as Modbus Slave With the software installed you can now open the Hardware Configuration and configure the CP341 in your rack. Double click the CP to open its properties and click on the Parameter button. The Point to Point configuration software will now open.
From the drop down box at the top left, select Modbus Slave as the Protocol. Next double click the Protocol icon in the middle of the screen. S7-300 Slave Configure the Driver.
You are now presented with a number of tabs. The first tab 'General' shows the driver versions in use. This is for information only. The second tab 'Modbus-Slave' allows you to define the communications properties of the system, baud, stop bits etc. S7-300 Slave Configure the Driver.

On the tab labelled FC01, 05, 15, you can enter the Modbus address ranges to be mapped into M area, Outputs, Timers and Counters. If any areas are not used, enter 0. S7-300 Slave Configure the Driver. On the tab FC02, you can define the mapping for M area and Inputs to be read from.
S7-300 Slave Configure the Driver. On the tab FC03, 06, 16 you only need to enter a DB number. These function codes use the address range starting from Modbus address The DB number specified is the start DB of a range of DB's that are generated by the user and must be 512 words long. If your Modbus address is say 40513, you would need to generate another consecutively numbered DB of 512 words long. Modbus address would be the first address in the second DB (word 0 of the second DB, the 513 word in total). S7-300 Slave Configure the Driver.
The tab labelled FC4 is configured in the same way but for the address range. S7-300 Slave Configure the Driver. The next tab is labelled 'Limits'. This is where you can define the range of DB's, Memory and Outputs to be written to by FC05, FC15, FC06 and FC16. If you were to use the Modbus address 40513, this would reside in the second DB at word 0. You would therefore need to set the limits here to DB1 and DB2 (assuming DB1 is the DB selected for use by FC03, 06, 16). This is similar for M and Q areas.